Unvested shares are commonly granted in exchange for services from employees or non-employees. Generally, if an entity receives services as consideration for its own equity instruments, then IFRS 2 Share-based Payment applies. Under IFRS 2, vesting conditions are either service conditions or performance conditions. Service conditions require the counterparty to complete a specified period of service. Performance conditions require the counterparty to complete a specified period of service and to meet specified performance targets while rendering the services; a performance condition can be either a market condition or a non-market performance condition. [see IFRS 2 Definition]
Ordinary shares that are subject to recall – i.e. contingently returnable – are dealt with in the same way as unvested ordinary shares for EPS purposes. [IAS 33.24, IAS 33.48]
This chapter covers unvested ordinary shares whose vesting is conditional only on satisfying service conditions. Unvested shares subject to performance conditions are regarded as contingently issuable ordinary shares for EPS purposes and are subject to specific requirements (see Contingently issuable ordinary shares).
This chapter does not deal with:
- shares that are issuable for more than little or no cash consideration (see Options, warrants and their equivalents); or
- contracts that may be settled either in shares or in cash (see Contracts that may be settled in shares or in cash).
Additional considerations in the context of share-based payment arrangements are set out in EPS Impact of share-based payments.
EPS implications
The EPS implications of ordinary shares issued in exchange for services depend on when the ordinary shares are granted and vested.
|
Consider when the ordinary shares are granted or vested |
|
|
↓ |
↓ |
|
Include in basic EPS the fraction entitled to dividends |
Include as equivalent of options in diluted EPS the fraction not entitled to dividends |
|
Potential impact on basic EPS |
Potential impact on diluted EPS |
|
The numerator might or might not be affected, the denominator is not affected. |
The numerator might or might not be affected, the denominator is affected. |
|
Unvested ordinary shares are not regarded as outstanding until they are vested. Ordinary shares issued as compensation for services received are included in the denominator as the services are received. [IAS 33.21(g)] Ordinary shares may be entitled to non-forfeitable dividends during the vesting period. If this is the case, then to the extent that these dividends have not been recognised in profit or loss, in our view the numerator should be adjusted for these dividends and any undistributed earnings attributable to these shares, in accordance with their participating rights. This is because the numerator is intended to reflect amounts that are attributable to outstanding ordinary shares, and unvested shares are not regarded as outstanding. [IAS 33.10, IAS 33.24, IAS 33.A13–A14] |
Unvested ordinary shares are treated as options in diluted EPS. Generally, no adjustment is necessary in the numerator because unvested ordinary shares and shares subject to recall are classified as equity. However, to the extent that these shares are entitled to dividends, adjustments to basic EPS (see left) are added back to the numerator in diluted EPS. The potential adjustment to the denominator is determined using the treasury share method. [IAS 33.48] |
Dilutive or anti-dilutive?
Because unvested ordinary shares are treated as options in diluted EPS, they are generally dilutive if the average market price of ordinary shares during the period exceeds the assumed proceeds (generally, the fair value of services to be supplied to the entity in the future).
However, to the extent that these shares are entitled to dividends, the numerator may also be impacted by the adjustments in basic EPS that are added back to the numerator for diluted EPS (see above). In such cases, the shares may be anti-dilutive even if the market price of ordinary shares exceeds the assumed proceeds.
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The following basic facts relate to Company P.
The following facts are also relevant for this example.
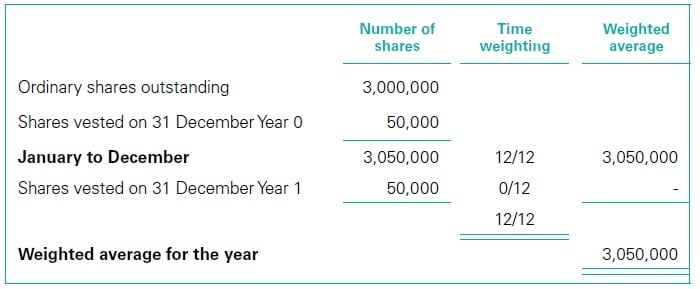
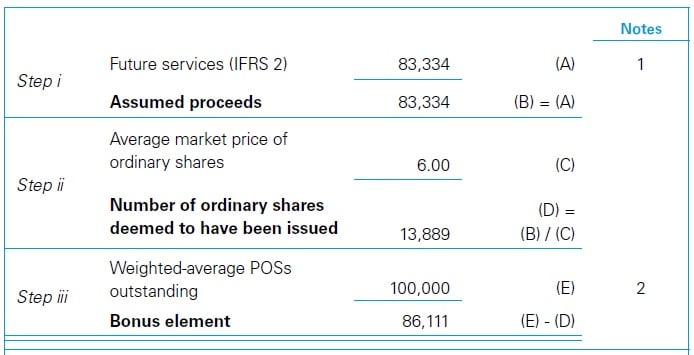
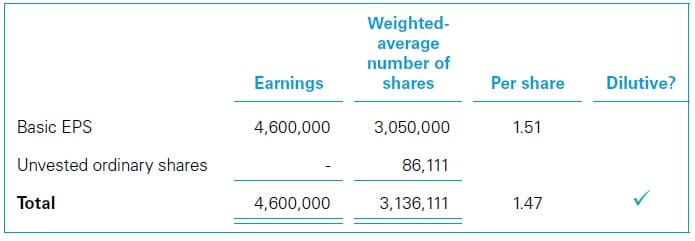
WorkingsThe EPS computations for Year 1 are as follows.
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
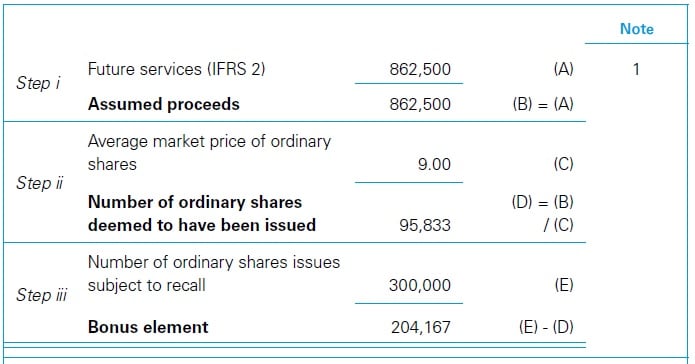
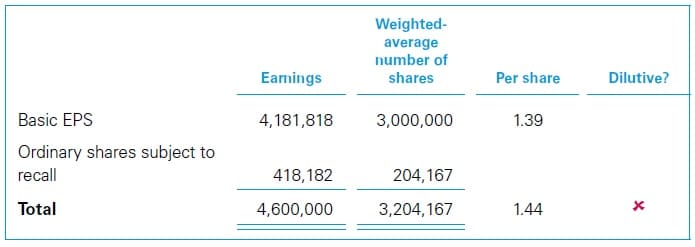
The basic facts are the same as in the above case – Unvested ordinary shares – Without dividend entitlement. The following facts are also relevant for Year 1.
Workings Year 1
The EPS computations for Year 1 are as follows.
|
Annualreporting provides financial reporting narratives using IFRS keywords and terminology for free to students and others interested in financial reporting. The information provided on this website is for general information and educational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for professional advice. Use at your own risk. Annualreporting is an independent website and it is not affiliated with, endorsed by, or in any other way associated with the IFRS Foundation. For official information concerning IFRS Standards, visit IFRS.org or the local representative in your jurisdiction.
Unvested ordinary shares Unvested ordinary shares Unvested ordinary shares Unvested ordinary shares Unvested ordinary shares Unvested ordinary shares