Last update 18/12/2019
Introduction IFRS 17 Insurance contracts – More than 20 years in development, IFRS 17 represents a complete overhaul of accounting for insurance contracts. The new standard applies a current value approach to measuring insurance contracts and recognises profit as insurers provide services and are released from risk. The profit or loss earned from underwriting activities are reported separately from financing activities. Detailed note disclosures explain how items like new business issued, experience in the year, cash receipts and payments, and changes in assumptions affected the performance and the carrying amount of insurance contracts.
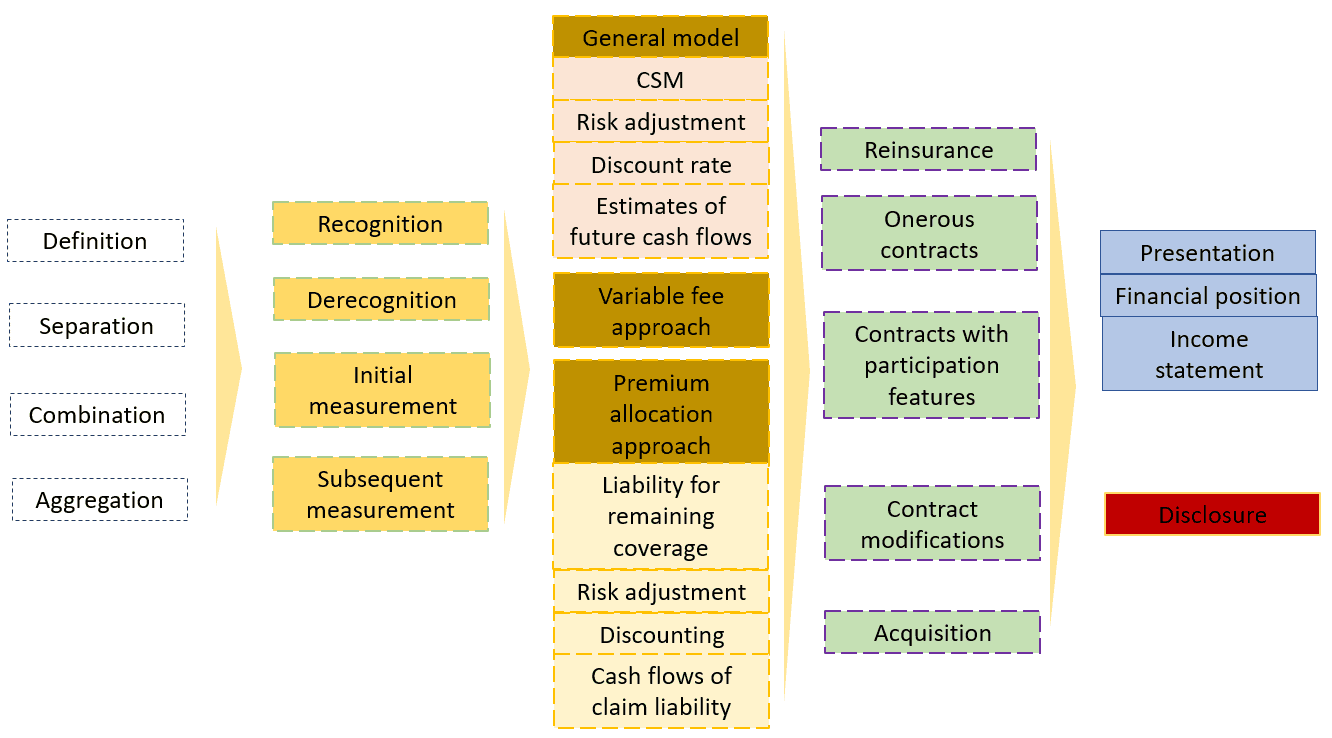
IFRS 17 establishes principles for the recognition, measurement, presentation and disclosure of insurance contracts issued, reinsurance contracts held and investment contracts with discretionary participation features an entity issues.

|
Definition |
Insurance contracts are contracts under which the issuer (insurer) accepts significant insurance risk from another party (the policyholder) by agreeing to compensate the policyholder if a specified uncertain future event (the insured event) adversely affects the policyholder. Other important definitions are 1) Reinsurance contracts and 2) Investment contracts with discretionary participation features. |
| Some non-insurance components (embedded derivatives, distinct investment components and distinct (i.e., non-insurance ) goods or services) should be separated and accounted for using other IFRSs. Other important items are 1) financial guarantee contracts and 2) fixed-fee service contracts. | |
| Combination |
A set, or series, of insurance contracts with the same or a related counterparty, may achieve, or be designed to achieve, a single overall commercial effect. In order to report the substance of such contracts, it may be necessary to treat the set or series as a whole. |
|
The level of aggregation deals with grouping individual insurance contracts for the purposes of recognizing losses when a group of contracts is onerous and the timing of the recognition of profits arising from a group of profitable contracts. |
|
|
An insurance contract is initially recognized when the coverage periods begins or when the company concludes that the contract is onerous. |
|
| Derecognition |
When the obligations are extinguished or upon some contract modifications. |
|
An entity should measure the contractual service margin on initial recognition of a group of insurance contracts at an amount that results in no income or expenses arising from:
|
|
|
The insurer should remeasure the contracts using updated assumptions about cash flows, discount rate, and risk. The effect of changes in estimates relating to future service is recognized in the periods in which the service is actually provided. |
|
| Building Block Approach
|
The general approach is the Building Block Approach (BBA). BBA is based on the building blocks of:
The measurement must incorporate all available information about the expected cash flows related to fulfilling the insurance contract and must be consistent with observable market information. Options and guarantees must be reflected in the measurement of the insurance contracts. |
|
General model |
The general model measures a group of insurance contracts as the sum of the following ‘building blocks’:
|
| Variable fee approach |
IFRS 17 distinguishes between insurance contracts with and without direct participation features. The general model is modified for insurance contracts with direct participation features—those contracts are measured applying modified requirements referred to as the ‘variable fee approach’. Introduction IFRS 17 Insurance contracts |
|
Premium allocation approach |
The premium allocation approach is a simplified form of measuring insurance contracts in comparison with the general model. Use of the premium allocation approach is optional for each group of insurance contracts that meets the eligibility criteria. |
|
Reinsurance |
A reinsurance contract is an insurance contract issued by one entity (the reinsurer) to compensate another entity for claims arising from one or more insurance contracts issued by the other entity (underlying contracts). IFRS 17 requires a reinsurance contract held to be accounted for separately from the underlying insurance contracts to which it relates. Introduction IFRS 17 Insurance contracts |
|
An insurance contract is onerous at the date of initial recognition if the fulfilment cash flows allocated to the contract, including any previously recognised acquisition cash flows and any cash flows arising from the contract at the date of initial recognition in total are a net outflow. Introduction IFRS 17 Insurance contracts |
|
|
Contracts with participation features |
Entities that issue contracts with participation features provide policyholders with a financial return on the premiums they pay by sharing the performance of underlying items with policyholders. Introduction IFRS 17 Insurance contracts |
|
An insurance contract may be modified, either by agreement between the parties or as result of regulation. If the terms are modified, an entity must derecognise the original insurance contract and recognise the modified contract as a new contract, when certain conditions are met. Introduction IFRS 17 Insurance contracts |
|
|
Insurance contracts acquired in a transfer or a business combination are classified and measured in the same way as those issued by the entity at the date of the combination or transfer, except that the fulfilment cash flows are recognised at that date. |
|
| Statement of Financial Position – Insurance contracts are presented as insurance contract liabilities or as insurance contract assets.
Income Statement – Insurance revenue less incurred claim expense equals the ‘insurance service result’, as the gross profit. Investment income less insurance finance expenses equals ‘net financial result’. The effect of changes in discount rates on the insurance contract may be presented in Other Comprehensive Income (OCI) rather than in the income statement. Introduction IFRS 17 Insurance contracts |
|
|
Discloses information to enable financial statement users to assess the effect that contracts within the scope of IFRS 17 have on an entity’s financial position, financial performance and cash flows. IFRS 17 requires disclosure of qualitative and quantitative information about: Introduction IFRS 17 Insurance contracts |
|
|
Transition and other articles |
Topics: Introduction IFRS 17 Insurance contracts |
See also: The IFRS Foundation