Last update 18/03/2020
IFRS 7 Other price risks Step-by-step – Other price risks is part of the risk disclosures requirements under IFRS 7 Financial Instruments: Disclosures. Other price risks is part of market risk (the other main market risk categories being currency risk and interest rate risk) and is defined as the risk that the fair value or future cash flows of a financial instrument will fluctuate because of changes in market prices (other than those arising from interest rate risk or currency risk), whether those changes are caused by factors specific to the individual financial instrument or its issuer or by factors affecting all similar financial instruments traded in the market. IFRS 7 Other price risks Step-by-step
Management should disclose information that enables users of its financial statements to evaluate the nature and extent of risks arising from financial instruments to which the entity is exposed at the end of the reporting period [IFRS 7 31]. The disclosures require focus on the risks that arise from financial instruments and how they ha ve been managed. These risks typically include, but are not limited to, credit risk, liquidity risk and market risk [IFRS 7 32]. IFRS 7 Other price risks Step-by-step
ve been managed. These risks typically include, but are not limited to, credit risk, liquidity risk and market risk [IFRS 7 32]. IFRS 7 Other price risks Step-by-step
Qualitative and quantitative disclosures are required. Management should therefore disclose, for each type of risk arising from financial instruments:
- The exposures to risk and how they arise, and its objectives, policies and processes for managing the risk and the methods used to measure the risk (qualitative disclosure) [IFRS 7 33]; and IFRS 7 Other price risks Step-by-step
- Summary quantitative data about its exposure to that risk at the end of the reporting period (quantitative disclosures) [IFRS 7 34]. Market risk
If the quantitative data disclosed at the end of the reporting period is unrepresentative of an entity’s exposure to risk during the period, management should provide further information that is representative [IFRS 7 35]. IFRS 7 Other price risks Step-by-step
Table – Overview exposure to financial risks, possible disclosures and management of risk
|
Exposure arising from |
Possible disclosure |
Management of risk |
|
|
Market risk – Currency risk |
Future commercial transactions Recognised financial assets and liabilities not denominated in LC |
Cash flow forecasting |
Foreign currency forwards and foreign currency options |
|
Market risk – Interest rate risk |
Long-term borrowings at variable rates |
Interest rate swaps |
|
|
Market risk – Other price risks |
Investments in equity securities |
Sensitivity of equity financial instruments to equity index benchmark prices (also known as Beta) |
Portfolio diversification |
|
Cash and cash equivalents, trade receivables, derivative financial instruments, debt investments and contract assets |
Credit ratings |
Diversification of bank deposits, credit limits and letters of credit Investment guidelines for debt investments |
|
|
Borrowings and other liabilities |
Rolling cash flow forecasts |
Availability of committed credit lines and borrowing facilities |
Examples of other price risk are (among others): equity prices, credit spreads and commodity (including precious metal) prices, and variables that may be unobservable or only indirectly observable, such as volatilities and correlations. Market risk includes issuer risk and investment risk.
Issuer risk: the risk of loss from changes in fair value resulting from credit-related events affecting an issuer to which an entity is exposed through tradable securities or derivatives referencing the issuer
Investment risk: issuer risk associated with positions held as financial investments
Country risk: the risk of losses resulting from country-specific events. It includes transfer risk, whereby a country’s authorities prevent or restrict the payment of an obligation, as well as systemic risk events arising from country-specific political or macroeconomic developments
Disclosure example – Other price sensitivity IF RS 7 Other price risks Step-by-step
RS 7 Other price risks Step-by-step
[IFRS 7 33(a)-(b), IFRS 7 IG15, IFRS 7 40(a)-(b)] IFRS 7 Other price risks Step-by-step
The Group is exposed to other price risk in respect of its listed equity securities and the investment in XY Ltd (see Note 15.3).
For the listed equity securities, an average volatility of 20% has been observed during 2019 (2018: 18%). This volatility figure is considered to be a suitable basis for estimating how profit or loss and equity would have been affected by changes in market risk that were reasonably possible at the reporting date. If the quoted stock price for these securities increased or decreased by that amount, profit or loss and equity would have changed by CU 85 (2018: CU 62). IFRS 7 Other price risks Step-by-step
The investments in listed equity securities and in XY Ltd are considered long-term, strategic investments. In accordance with the Group’s policies, no specific hedging activities are undertaken in relation to these investments. The investments are continuously monitored and voting rights arising from these equity instruments are utilised in the Group’s favour.
Disclosure example – Commodity price risk IFRS 7 Other price risks Step-by-step
The Group is affected by the volatility of certain commodities. Its operating activities involve the ongoing purchase and manufacturing of electronic parts and therefore require a continuous supply of copper. Due to the significantly increased volatility of the price of the underlying, the Group’s Board of Directors has developed and enacted a risk management strategy dealing with commodity price risk and its mitigation. IFRS 7 Other price risks Step-by-step
Based on a 12-month forecast about the required copper supply, the Group hedges the purchase price using forward commodity purchase contracts. The forecast is deemed to be highly probable.
Forward contracts with a physical delivery which qualify for normal purchase, sale or usage are therefore not recognised as derivatives and are disclosed in Note 30.
Commodity price sensitivity IFRS 7 Other price risks Step-by-step
The following table shows the effect of price changes for copper after the impact of hedge accounting. IFRS 7 Other price risks Step-by-step
|
2012 IFRS 7 Other price risks Step-by-step |
Change in year-end price |
Effect on profit before tax |
Effect on equity |
|
IFRS 7 Other price risks Step-by-step IFRS 7 Other price risks Step-by-step Copper IFRS 7 Other price risks Step-by-step IFRS 7 Other price risks Step-by-step |
+15% |
-220 |
-585 |
|
-15% |
220 |
585 |
Disclosure example – Equity price risk IFRS 7 Other price risks Step-by-step
The Group’s listed and unlisted equity securities are susceptible to market-price risk arising from uncertainties about future values of the investment securities. The Group manages the equity price risk through diversification and placing limits on individual and total equity instruments. Reports on the equity portfolio are submitted to the Group’s senior management on a regular basis. The Group’s Board of Directors reviews and approves all equity investment decisions. (IFRS 7 33(b)) IFRS 7 Other price risks Step-by-step
At the reporting date, the exposure to unlisted equity securities at fair value was €1,163,000. A change of 10% in the overall earnings stream of the valuations performed could have an impact of approximately €120,000 on the equity of the Group. (IFRS 7 33(a), IFRS 7 40) IFRS 7 Other price risks Step-by-step
At the reporting date, the exposure to listed equity securities at fair value was €337,000. A decrease of 10% on the NYSE market index could have an impact of approximately €55,000 on the income or equity attributable to the Group, depending on whether or not the decline is significant or prolonged. An increase of 10% in the value of the listed securities would only impact equity, but would not have an effect on profit or loss. IFRS 7 Other price risks Step-by-step
Example – Equity exposure 1
The table below presents the carrying values of our equity investments according to IFRS definition split by trading and nontrading for the respective reporting dates. We manage our respective positions within our market risk and other appropriate risk frameworks.
Composition of our Equity Exposure
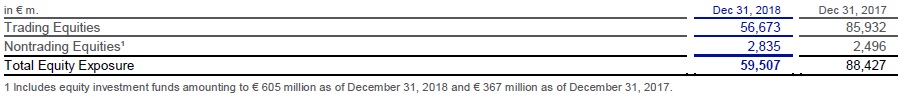
As of December 31, 2018, our Trading Equities exposure was mainly composed of € 54.3 billion from Corporate & Investment Bank activities and € 2.3 billion from Asset Management. Overall trading equities decreased by € 29.3 billion year on year driven mainly by decreased exposure in Corporate & Investment Bank activities.
See also: The IFRS Foundation