IFRS 11 Joint Arrangements quick overview provides the fastest overview on financial reporting by entities that have an interest in arrangements that are bound by a contractual arrangement providing two or more parties joint control.
OBJECTIVETo establish principles for financial reporting by entities that have an interest in arrangements that are controlled jointly (i.e. joint arrangements) IFRS 11 Joint Arrangements quick overview IFRS 11 Joint Arrangements quick overview IFRS 11 Joint Arrangements quick overview |
SCOPEIFRS 11 applies to all entities that are a party to a joint arrangement |
DEFINITIONSJoint operation – Joint operator |
|
JOINT ARRANGEMENTA joint arrangement is an arrangement |
|||
Comparability – An enhancing qualitative characteristic that enables users to identify and understand similarities in, and differences among, items.
The Conceptual Framework provides the following guidance [Conceptual Framework 2.24 – 2.29]:
Users’ decisions involve choosing between alternatives, for example, selling or holding an investment, or investing in one reporting entity or another. Consequently, information about a reporting entity is more useful if it can be compared with similar information about other entities and with similar information about the same entity for another period or another date.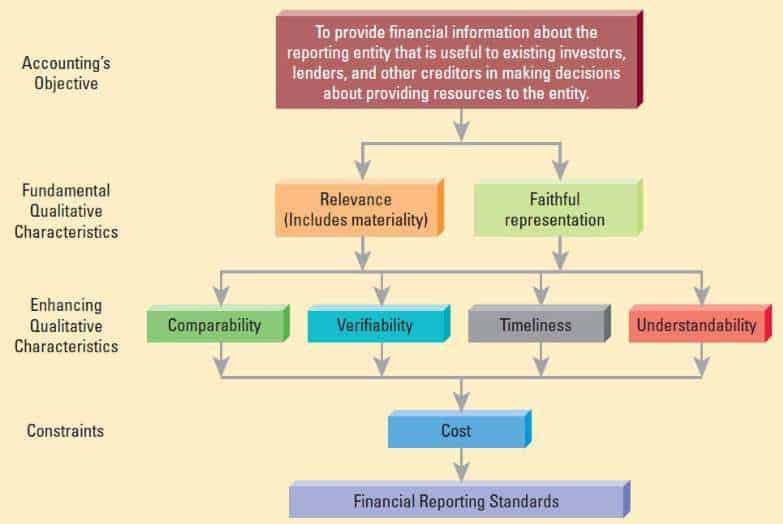
Comparing Financial Statements between companies is the qualitative characteristic that enables users to identify and understand similarities in, and differences among, items. Unlike the other qualitative characteristics, comparability does not relate to … Read more
Compound financial instruments – An incredible shift in accounting concepts
Compound financial instruments contain elements which are representative of both equity and liability classification.
A common example is a convertible bond, which typically (but not always, see ‘2 Convertible bonds‘ below) consists of a liability component in relation to a contractual arrangement to deliver cash or another financial asset) and an equity instrument (a call option granting the holder the right, for a specified period of time,
to convert the bond into a fixed number of ordinary shares of the entity).
Other examples of possible compound financial instruments include instruments with rights to a fixed minimum dividend and additional discretionary dividends, and instruments with fixed dividend rights but … Read more
IAS 32 Financial Instruments Presentation outlines the accounting requirements for the presentation of financial instruments, particularly as to the classification of such instruments into financial assets, financial liabilities and equity instruments. The standard also provide guidance on the classification of related interest, dividends and gains/losses, and when financial assets and financial liabilities can be offset.
Liabilities and equity
The issuer of a financial instrument shall classify the instrument, or its component parts, on initial recognition as a financial liability, a financial asset or an equity instrument in accordance with the substance of the contractual arrangement and the definitions of a financial liability, a financial asset and an equity instrument. IAS 32 Financial Instruments Presentation
The entity must on initial recognition … Read more
IAS 32 Clearly distinguishing liability and equity – When an entity issues a financial instrument, it must determine its classification either as a liability (debt) or as equity. That determination has an immediate and significant effect on the entity’s reported results and financial position. Liability classification affects an entity’s gearing ratios and typically results in any payments being treated as interest and charged to earnings.
Equity classification avoids these impacts but may be perceived negatively by investors if it is seen as diluting their existing equity interests. Understanding the classification process and its effects is therefore a critical issue for management and must be kept in mind when evaluating alternative financing options.
IAS 32 Financial Instruments: Presentation addresses this classification … Read more