Last update 31/12/2019
Foreign exchange reserve – Gains/losses arising on translating the net assets of overseas operations into CU.
IAS 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates outlines how to account for foreign currency transactions and operations in financial statements, and also how to translate financial statements into a presentation currency. An entity is required to determine a functional currency (for each of its operations if necessary) based on the primary economic environment in which it operates and generally records foreign currency transactions using the spot conversion rate to that functional currency on the date of the transaction.
This reserve results from translating the financial statements of foreign operations to include these financial statement in the consolidated financial statements. The foreign exchange reserve exists to restrict the parent company’s ability to pay dividend to it owners (because the foreign exchange reserve reduces retained earnings).
The translation arising on the acquisition of a foreign operation is recorded in equity of the parent company’s consolidated balance sheet. Subsequent difference arising on the translation of a foreign operation at a reporting date is recorded in equity of the parent company’s consolidated income in other comprehensive income. Disposal see below.
The foreign exchange reserve is described in IAS 21 52(b): Net exchange differences recognised in other comprehensive income and accumulated in a separate component of equity, and a reconciliation of the amount of such exchange differences at the beginning and end of the period.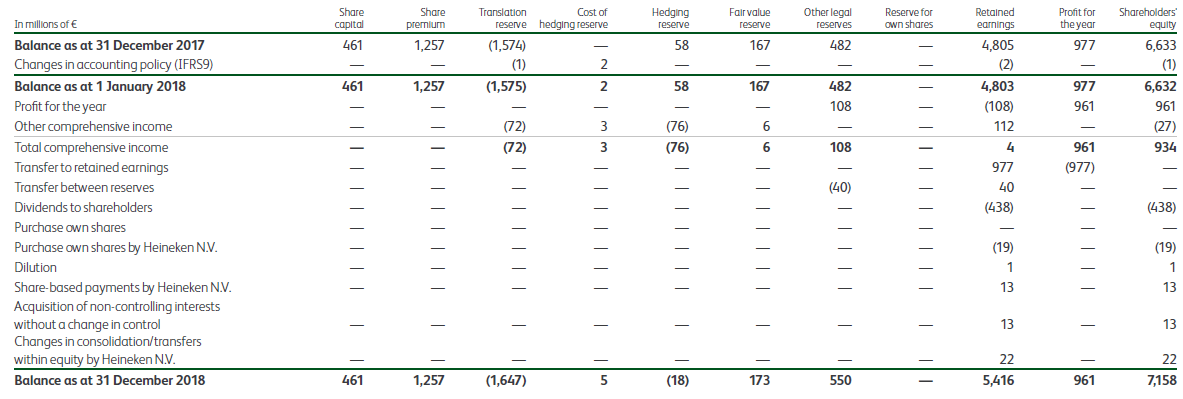

Disposal of foreign operations
IFRS 10 B98 Disposal results in loss of control
Reclassify the cumulative foreign exchange reserve in equity relating to the parent through OCI to P/L as a reclassification adjustment. [IAS 21 48]
Dr Foreign exchange reserve (OCI)
Cr Reclassification adjustment (P/L)
IFRS 10 B96 Disposal does not result in loss of control
Re-attribute the proportionate share of the cumulative amount of the foreign exchange reserve to non-controlling interest.
Dr Foreign exchange reserve (Equity holders of the company)
Cr Foreign exchange reserve (Non-controlling interest)
Example translation of equity
The financial statements of the recently acquired subsidiary XYZ are made for the period ended as at 30 June 20×1 and are to be included in the consolidated financial statements of Parent as at the same date.
Parent has acquired 80% of subsidiary XYZ on 1 July 20×0, the starting date of the current reporting period close. The applicable exchange rate are:
1 July 20×0: CU 10.00
Average rate: CU 11.25
30 June 20×1: CU 12.50
|
DT (CR) |
Amount (FC) |
Rate |
Amount (CU) |
|
Share capital |
-100,000 |
10.00 |
-1,000,000 |
|
Retained earnings |
|||
|
– at acquisition |
-20,000 |
10.00 |
-200,000 |
|
– current year income |
-40,000 |
11.25 |
-337,500 |
|
Subtotal |
-160,000 |
-1,537,500 |
|
|
Goodwill |
4,000 |
10.00 |
40,000 |
|
Total equity |
-164,000 |
-1,577,500 |
|
|
Machinery – carrying value |
140,000 |
12.50 |
1,750,000 |
|
Inventory |
6,000 |
12.50 |
75,000 |
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
4,000 |
12.50 |
50,000 |
|
Total assets less liabilities |
-160,000 |
1,875,000 |
|
|
Total |
– |
n/a |
297,500 |
|
Foreign exchange reserve |
-297,500 |
Foreign exchange reserve allocation to non-controlling interest
|
DT (CR) |
Amount (FC) |
Rate |
Amount (CU) |
|
Acquisition (share capital 100,000, retained earnings 20,000 and goodwill 4,000) |
124,000 |
10.00 |
1,240,000 |
|
Equity holders of the company |
80.00 |
1,000,000 |
|
|
Non-controlling interest |
20.00 |
240,000 |
|
|
Current year income |
40,000 |
11.25 |
337,500 |
|
Equity holders of the company |
80.00 |
270,000 |
|
|
Non-controlling interest |
20.00 |
67,500 |
|
|
Closing equity |
|||
|
Equity attributable to equity holders |
1,270,000 |
||
|
Non-controlling interest |
307,500 |
||
|
Total equity |
1,577,500 |
||
Some useful definitions:
Average rate is the mean of the exchange rates in force during a period, used to translate period statements (income and cash flow)
Closing rate is the exchange rate at the balance sheet date, used to translate position statements (balance sheet and changes in equity)
Exchange difference is the difference resulting from reporting the same number of units of a foreign currency in the reporting currency at different exchange rates.
Foreign currency is a currency other than the reporting currency of an enterprise.
Foreign operation is a subsidiary, associate, joint venture or branch of the reporting enterprise, the activities of which are based or conducted in a country other than the country of the reporting enterprise.
See also: The IFRS Foundation


Foreign exchange reserve