(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
Presentation of financial statements
This is a summary of IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements starting with a pictured overview and then a more detailed narrative touching the most important reporting issues for this subject.
(Source https://www.bdo.global/en-gb/services/audit-assurance/ifrs/ifrs-at-a-glance)
IAS 1 Basis of preparation of financial statements
IFRS Reference: IAS 1
Overview
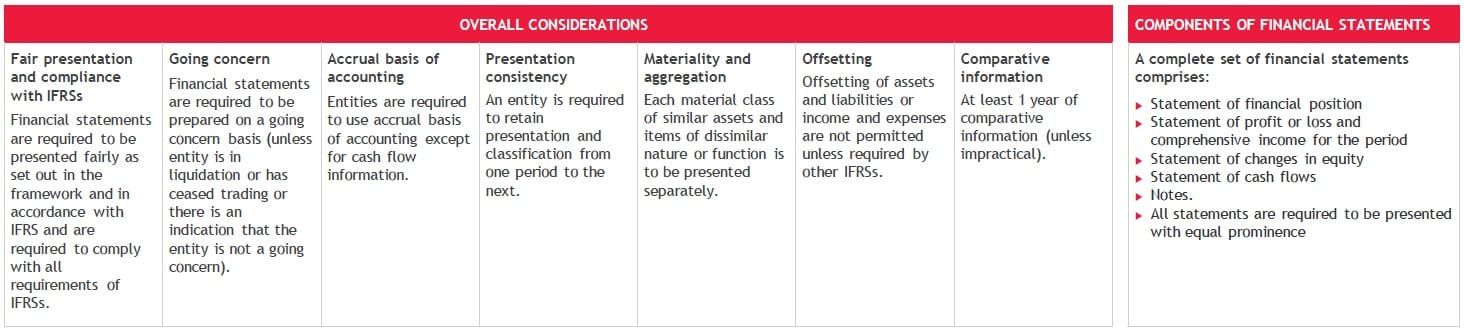
Financial statements are prepared on a going concern basis, unless management intends or has no realistic alternative other than to liquidate the entity or to stop trading.
If management concludes that the entity is a going concern, but there are nonetheless material uncertainties that cast significant doubt on the entity’s ability to continue as a going concern, then the entity discloses those uncertainties.
In carrying out its assessment of going concern, management considers all available information about the future for at least, but not limited to, 12 months from the reporting date. This assessment determines the basis of preparation of the financial statements.
If the entity is not a going concern and the financial statements are being prepared in accordance with IFRS Standards, then in our view there is no general dispensation from their measurement, recognition and disclosure requirements.
Going concern assessment
Financial statements are prepared on a going concern basis, unless management intends or has no realistic alternative other than to liquidate the entity or to stop trading. [IAS 1.25]
Management assesses the entity’s ability to continue as a going concern for the purpose of determining the basis of preparation of the financial statements. [IAS 1.25]
In assessing whether the going concern assumption is appropriate, management assesses all available information about the future for at least, but not limited to, 12 months from the reporting date. [IAS 1.26]
IFRS Standards are not prescriptive about the events and conditions that should be considered as part of the going concern assessment.
If an entity ceases to be a going concern after the reporting date but before the financial statements are authorised for issue, then the financial statements are not prepared on a going concern basis. [IAS 1.25–26, IAS 10.14]
Disclosures about the going concern assessment
If management concludes that the entity is a going concern, but there are nonetheless material uncertainties that cast significant doubt on the entity’s ability to continue as a going concern, then the entity discloses those uncertainties.
Even if there are no material uncertainties about an entity’s ability to continue as a going concern, an entity discloses any significant judgements made in reaching this conclusion (a ‘close call’ scenario). [IAS 1.25, IAS 1.122]
Entity is not a going concern
If the entity is not a going concern but the financial statements are being prepared in accordance with IFRS Standards, then in there is no general dispensation from their measurement, recognition and disclosure requirements.
Even if the going concern assumption is not appropriate, IFRS Standards should be applied, with particular attention paid to the requirements for assets that are held for sale (see Assets that are held for sale), the classification of debt and equity instruments (see Equity and financial liabilities), the impairment of non-financial assets (see Impairment) and the recognition of provisions (see Recording provisions).
For an entity in liquidation, all liabilities continue to be recognised and measured in accordance with the applicable standard until the obligations are discharged or cancelled or expire (see Provisions, contingent assets and liabilities and recognition and derecognition).
Liquidation of a subsidiary is imminent
A subsidiary (that is still controlled by the parent – see Consolidation) may be expected to be liquidated and its financial statements be prepared on a non-going concern basis.
If the parent is expected to continue as a going concern, then in our view the consolidated financial statements should be prepared on a going concern basis. Common opinion is that the subsidiary should continue to be consolidated until it is liquidated or otherwise disposed of.
IAS 1 Form and components of financial statements
Overview
An entity with one or more subsidiaries presents consolidated financial statements unless specific criteria are met.
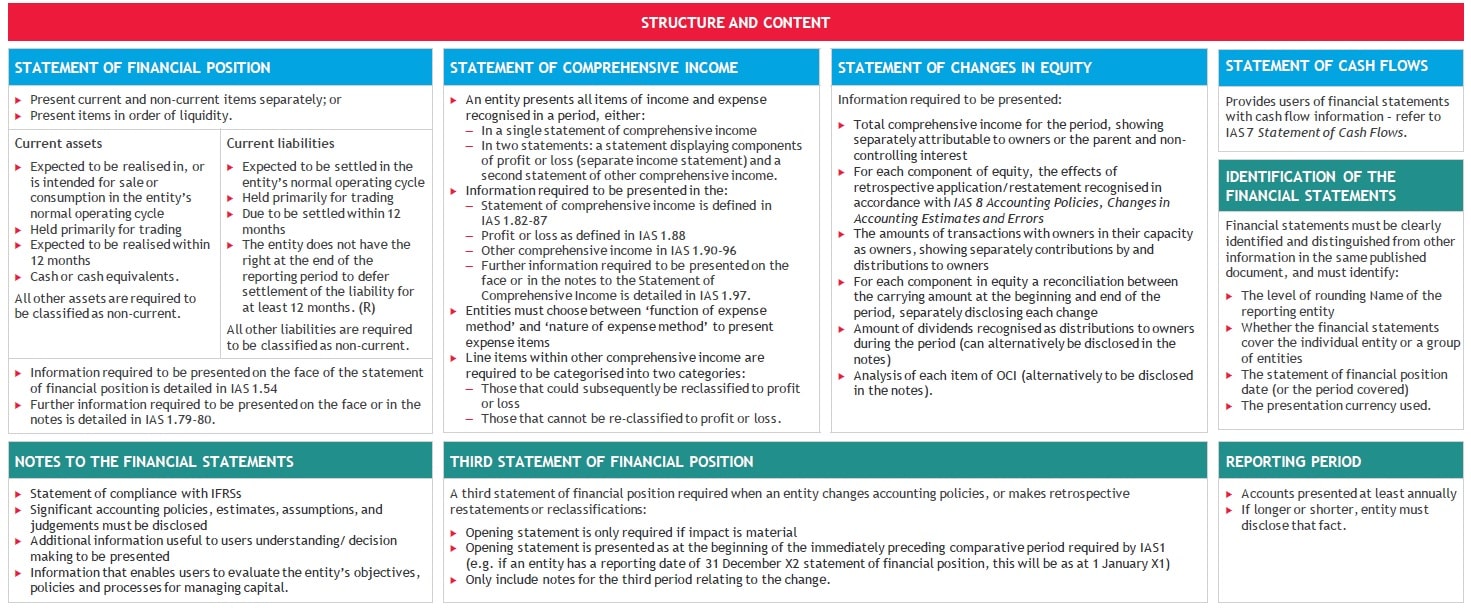
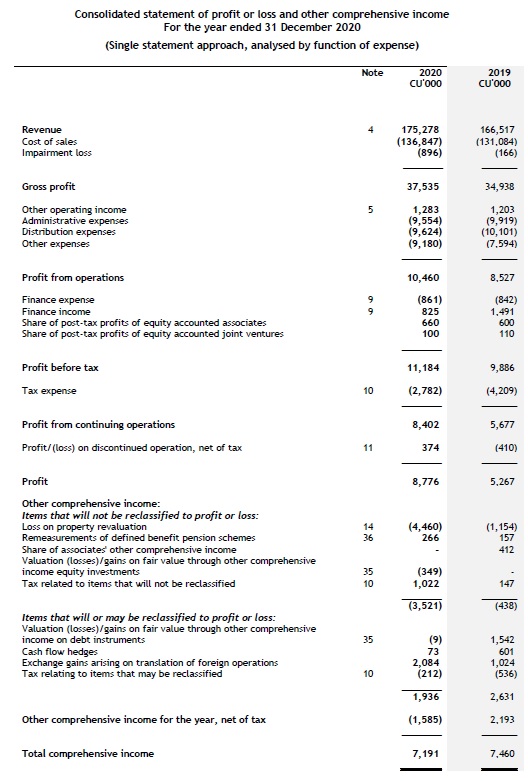
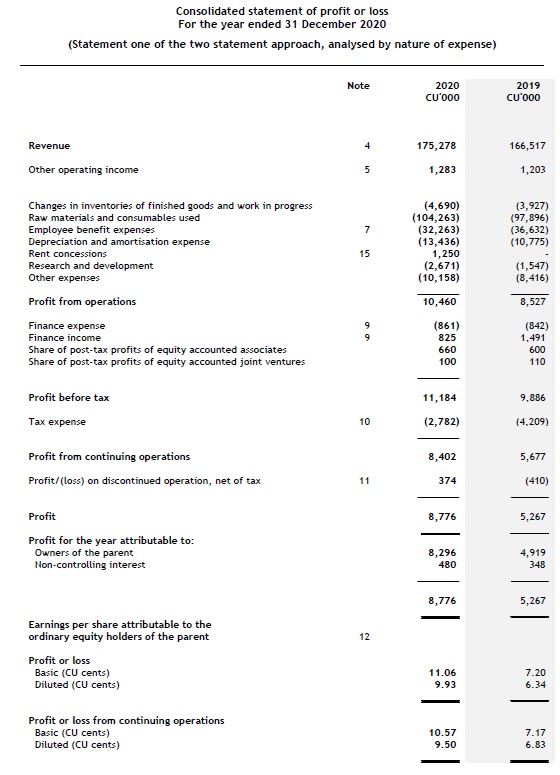
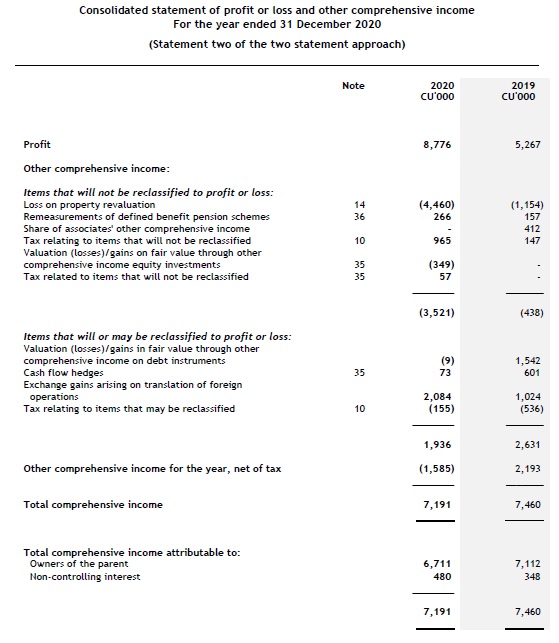
A complete set of financial statements consists of a statement of financial position; a statement of profit or loss and other comprehensive income; a statement of changes in equity; a statement of cash flows; and notes, including accounting policies.
All owner-related changes in equity are presented in the statement of changes in equity, separately from non-owner changes in equity.
IFRS Standards specify minimum disclosures for material information; however, they do not prescribe specific formats.
Comparative information is required for the preceding period only, but additional periods and information may be presented.
In addition, a statement of financial position as at the beginning of the preceding period is presented when an entity restates comparative information following a change in accounting policy, the correction of an error, or the reclassification of items in the statement of financial position.
Consolidated financial statements
A parent entity presents consolidated financial statements unless it is an investment entity that is required to measure all of its subsidiaries at FVTPL (see Investment entity consolidation exemption), or all of the following criteria are met:
- the parent is a wholly owned subsidiary, or is a partially owned subsidiary and its other owners (including those not otherwise entitled to vote) have been informed about, and do not object to, the parent not preparing consolidated financial statements;
- the parent’s debt or equity instruments are not traded in a public market (a domestic or foreign stock exchange or an over-the-counter market, including local and regional markets) – see Operating segments;
- the parent has not filed, nor is it in the process of filing, its financial statements with a securities commission or other regulatory organisation for the purpose of issuing any class of instruments in a public market; and
- the ultimate or any intermediate parent of the parent produces financial statements that are available for public use and comply with IFRS Standards, such that subsidiaries are either consolidated or measured at FVTPL. [IFRS 10.4(a), IFRS 10.4B]
Reporting period
Financial statements are presented for the reporting period ending on the date of the statement of financial position (reporting date). [IAS 1.10]
The reporting date may change in certain circumstances – e.g. following a change of major shareholder. When the reporting date changes, the annual financial statements are presented for a period that is longer or shorter than a year; there is no requirement to adjust historical comparative information. [IAS 1.36]
The following is presented as a complete set of financial statements:
- a statement of financial position (see Statement of financial position);
- a statement of profit or loss and OCI (see Statement of profit or loss and OCI);
- a statement of changes in equity (see below and Statement of changes in equity);
- a statement of cash flows (see Statement of cash flows); and
- notes to the financial statements, comprising significant accounting policies (see notes) and
- other explanatory information. [IAS 1.10]
An entity presents both a statement of profit or loss and OCI and a statement of changes in equity as part of a complete set of financial statements. These statements cannot be combined. [IAS 1.10]
Although IFRS Standards specify disclosures to be made in the financial statements, they do not prescribe formats or order of notes. However, notes need to be presented in a systematic manner, to the extent practicable.
Although a number of disclosures are required to be made in the financial statements, IFRS Standards generally allow flexibility in presenting additional line items and subtotals when such information is relevant to an understanding of the entity’s financial performance. [IAS 1.85, 113]
Disclosures that are not material need not be included in the financial statements, even if a standard includes a specific requirement or describes it as a minimum requirement. [IAS 1.31, BC30H–BC30I]
In addition to the information required to be disclosed in the financial statements, many entities provide additional information outside the financial statements, either because of local regulations or stock exchange requirements, or voluntarily (see chapter 5.8). [IAS 1.13, 54–55A, 82–85B]
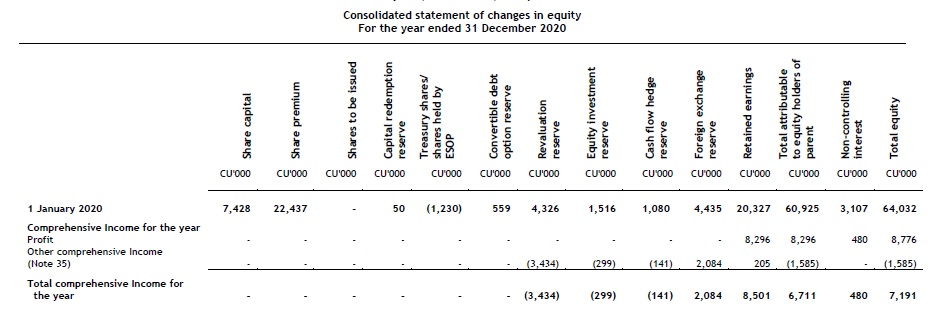
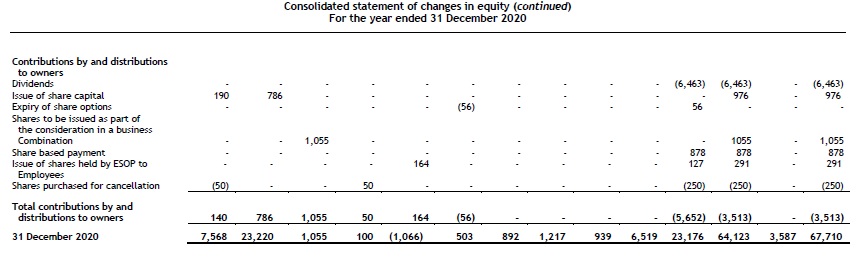
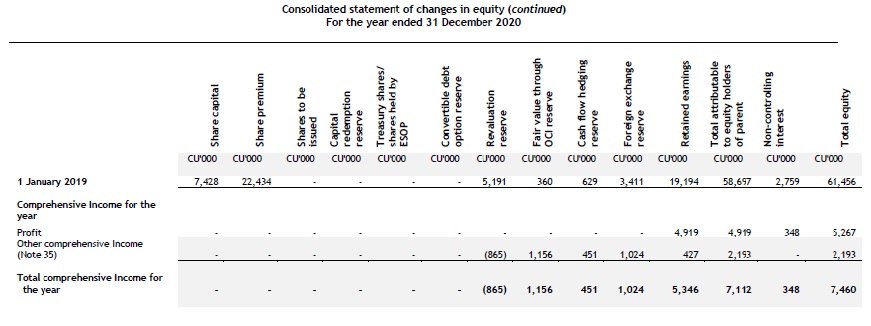
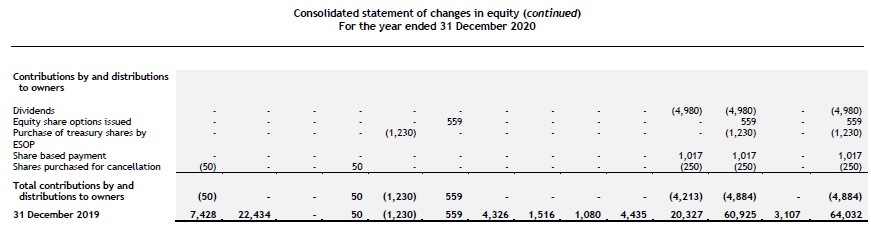
Statement of changes in equity
The following information is presented in the statement of changes in equity:
- profit or loss and total comprehensive income for the period, showing separately for profit or loss and OCI the total amounts attributable to owners of the parent and to NCI;
- for each component of equity, the effects of retrospective application or retrospective restatement recognised in accordance with the standard on accounting policies, changes in estimates and errors (see chapter 2.8); and
- for each component of equity, a reconciliation between the carrying amount at the beginning and at the end of the period, separately (as a minimum) disclosing changes resulting from:
- profit or loss;
- OCI; and
- transactions with owners in their capacity as owners, showing separately contributions by and distributions to owners and changes in ownership interests in subsidiaries that do not result in a loss of control. [IAS 1.106]
For each component of equity, an entity presents an itemised analysis of OCI. This analysis may be presented either in the statement of changes in equity or in the notes to the financial statements. [IAS 1.106A]
The notes to the financial statements include a separate schedule showing the effects of any changes in a parent’s ownership interest in a subsidiary that do not result in a loss of control. [IFRS 12.18]
Dividends and related per-share amounts are disclosed either in the statement of changes in equity or in the notes to the financial statements. [IAS 1.107]
Capital disclosure
An entity discloses information that enables users of its financial statements to evaluate the entity’s objectives, policies and processes for managing capital. [IAS 1.134]
Comparative information
Comparative information is required for the immediately preceding period only, but additional periods and information may be presented. [IAS 1.38]
A third statement of financial position is presented as at the beginning of the preceding period following a retrospective change in accounting policy, the correction of an error or a reclassification that has a material effect on the information in the statement of financial position. In general, the third statement of financial position is required only if it is material to users of the financial statements. [IAS 1.10(f), 40A–40D]
Unless there is a specific exemption provided in an IFRS standard, an entity discloses comparative information in respect of the previous period for all amounts reported in the current period’s financial statements.
Generally, the previous period’s related narrative and descriptive information is required only if it is relevant for an understanding of the current period’s financial statements and regardless of whether it was provided in the prior period. [IAS 1.38, 2.70]
Restatements and retrospective adjustments
Restatements and retrospective adjustments are presented as adjustments to the opening balance of retained earnings, unless an IFRS standard requires retrospective adjustment of another component of equity.
IFRS Standards require disclosure in the statement of changes in equity of the total adjustment to each component of equity resulting from changes in accounting policies, and separately from corrections of errors. [IAS 1.106(b), 110]
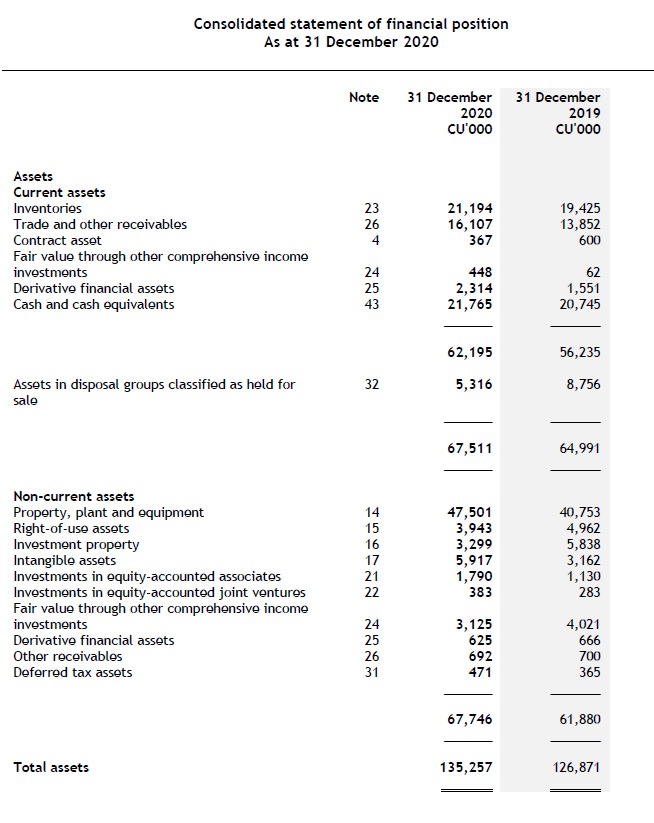
Statement of financial position
Statement of profit or loss and OCI
Statement of changes in equity
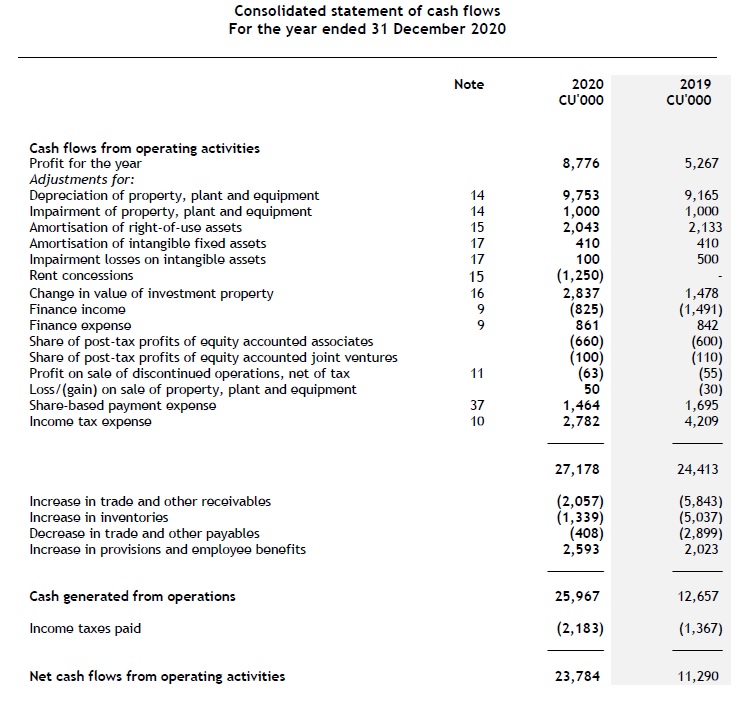
Statement of cash flows
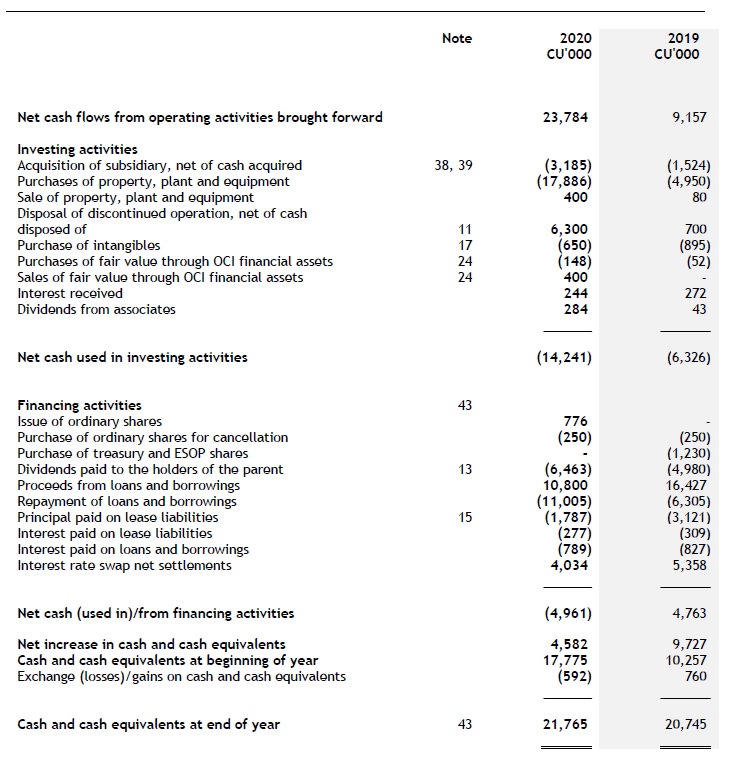
Notes to the financial statements, comprising significant accounting policies and other explanatory information

Presentation of financial statements
Presentation of financial statements
Annualreporting provides financial reporting narratives using IFRS keywords and terminology for free to students and others interested in financial reporting. The information provided on this website is for general information and educational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for professional advice. Use at your own risk. Annualreporting is an independent website and it is not affiliated with, endorsed by, or in any other way associated with the IFRS Foundation. For official information concerning IFRS Standards, visit IFRS.org or the local representative in your jurisdiction.
Related IFRS posts
Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements
Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements
Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements Presentation of financial statements