Last update 26/11/2019
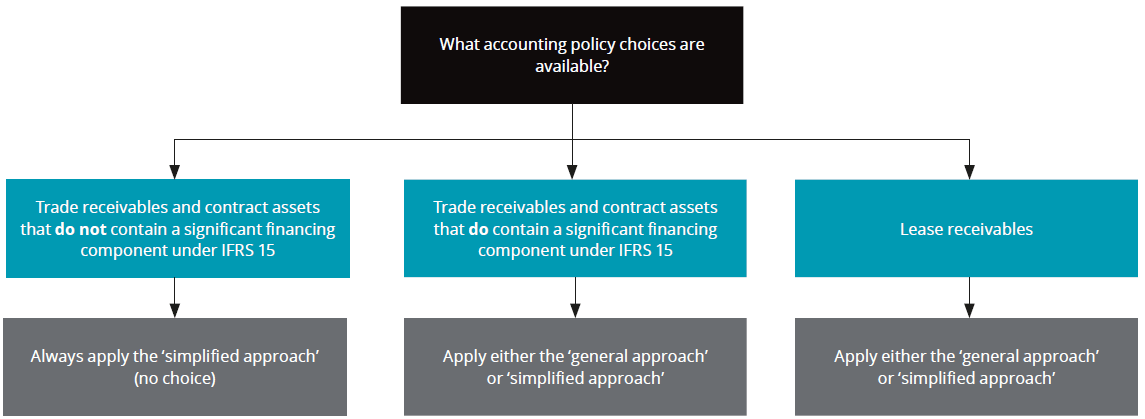
Accounting policy choices impairment of financial assets describes the impairment models available for trade receivables and contract assets with or without a significant financing component and lease receivables.
The impairment decisions
For trade receivables and contract assets that do not contain a significant financing component, it is a requirement to recognise a lifetime expected loss allowance (i.e. an entity must always apply the ‘simplified approach’). For other trade receivables, other contract assets, operating lease receivables and finance lease receivables it is an accounting policy choice that can be separately applied for each type of asset (but which applies to all assets of a particular type).

Link to ‘simplified approach‘ or ‘general approach‘
What is a significant financing component? Accounting policy choices impairment of financial assets
|
IFRS |
Rules Accounting policy choices impairment of financial assets |
|
A significant financing component exists if the timing of payments agreed to by the parties to the contract (either explicitly or implicitly) provides the customer or the entity with a significant benefit of financing the transfer of goods or services to the customer. |
|
|
A contract with a customer would not have a significant financing component if any of the following factors exist:
|
|
|
IFRS 15 has practical expedients whereby an entity need not adjust the promised amount of consideration for the effects of a significant financing component if the entity expects, at contract inception, that the period between when the entity transfers a promised good or service to a customer and when the customer pays for that good or service will be one year or less. It seems likely that this will apply for the majority of trade receivables. |
Other definitions:

Trade receivables
Trade receivables are amounts billed by a business to its customers when it delivers goods or services to them in the ordinary course of business. These billings are typically documented on formal invoices, which are summarized in an accounts receivable aging report. This report is commonly used by the collections staff to collect overdue payments from customers.
Contract assets
Contract asset is the term defined in IFRS 15 as an entity’s right to consideration in exchange for goods or services that the entity has transferred to a customer, when that right is conditioned on something other than the passage of time, for example the entity’s future performance. Accounting policy choices impairment of financial assets

 Lease receivables
Lease receivables
Lease receivables are very similar to the two other definitions above, they are receivables billed by a business to its customers when periodic payments on a lease contract are due (many times on a monthly basis). Lease receivables constitute a mix of costs and profit charges by a lease company to a lessee. Cost are operational costs (maintenance and/or gasoline), insurances, government taxes and the purchase of an underlying asset. Accounting policy choices impairment of financial assets
See also: The IFRS Foundation
![]()
![]()
Accounting policy choices impairment of financial assets
Accounting policy choices impairment of financial assets Accounting policy choices impairment of financial assets

