Last update 06/08/2019
The risk that the fair value or future cash flows of a financial instrument will fluctuate because of changes in foreign exchange rates.
Currency risk (or foreign exchange risk) arises on financial instruments that are denominated in a foreign currency, ie in a currency other than the functional currency in which they are measured. For the purpose of this IFRS, currency risk does not arise from financial instruments that are non-monetary items or from financial instruments denominated in the functional currency. [IFRS 7 B23]
A sensitivity analysis is disclosed for each currency to which an entity has significant exposure. [IFRS 7 B24]
The disclosure of currency risk is part of the capital and/or risk management strategy of an entity. Entities tend disclose a significant amount of text and tables to facilitate users of financial statements with lots of opportunities for analysing and comparing this data. Captions in the capital and/or risk management caption in the notes to the financial statements are:
- Hedging and financial derivatives,
- Currency risk,
- Interest-rate risks,
- Share-price risks,
- Other price risks,
- Credit risks,
- Liquidity risks.
Here is an exhibit from the Bosch Annual report 2017:
Currency risk
Currency risks of the operative business are mitigated by the central management of selling and purchasing currencies. The currency risk is determined on the basis of the worldwide consolidated cash flow in the respective currencies. Based on the business plan, estimated inflows and outflows in the various countries for the planning period are aggregated in a foreign exchange balance plan. The resulting net position is used for the central management of currency exposures.
The largest net currency positions of the planned cash flow are in CNY, GBP, and USD.
Hedging largely takes the form of forward exchange contracts; currency options and currency swaps to secure group financing are used to a lesser extent. These transactions, which are only entered into with banks, are subject to minimum requirements with respect to nature, scope, and complexity.
The risk attaching to material operating foreign currency items is determined using the value-at-risk concept, supplemented by worst-case analyses. These risk analyses and the hedge result are determined monthly and presented to management.
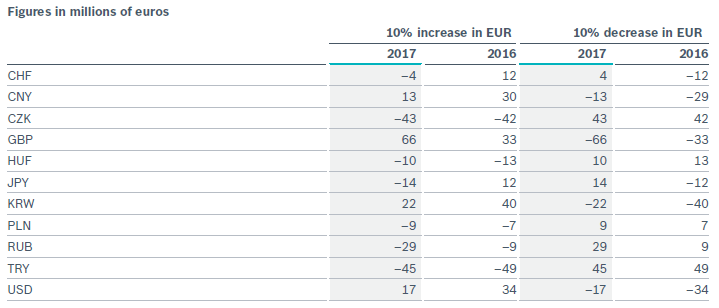
To present the currency risks in accordance with IFRS 7 Financial Instruments: Disclosures for the most important foreign currencies, all monetary assets and monetary liabilities denominated in foreign currency for all consolidated companies were analysed at balance sheet date and sensitivity analyses carried out for the respective currency pairs, in terms of the net risk.
A change in the EUR of 10 percent (taking the closing rate as the baseline) against the foreign currencies listed in the table would have the following implications for the profit before tax:



Currency risk
Currency risk
Currency risk Currency risk Currency risk Currency risk Currency risk